Shapefile
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
-
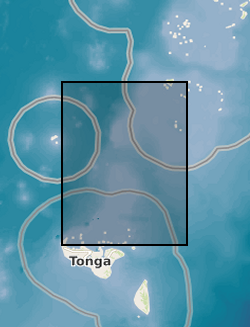
Tsunami trimlines identified across different islands of the Tonga archipelago. Trimlines have been used as a reference land feature following the January 2022 Tonga tsunami event that ripped off vegetation and built-up areas. Trimlines are distinctive limits between an area with sand coverage, vegetation destruction, and soil erosion on the one hand, and the unaffected natural vegetation on the other. This distinction provides a good landmark to map the inundation width and the landward extension of tsunami runup. In this case, the trimlines have been manually delineated by BGS - Earth Observation team using different high-resolution satellite datasets both optical (KompSat, Planet, Pleiades, WorldView) and radar (TerraSAR-X). Trimlines are well known from task-force publications documenting recent tsunami detection efforts and provide key information to support tsunami triggering mechanism models. For more info, see https://www.usgs.gov/media/images/tsunami-terms and Scheffers et al. (2012), https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9691-6
-
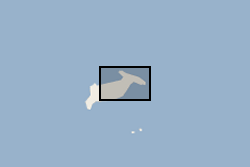
Waterlines have been extracted to delimit the edge of the Hunga Tonga - Hunga Ha'apai island between April 2017 and April 2022. Waterline is defined as the instantaneous land - water boundary at the time of the imaging process. Waterlines have been generated by BGS - Earth Observation team through a thresholding-based classification based on Sentinel-2 multispectral imagery and developed on Google Earth Engine. Specifically, the thresholding has been applied to the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) has been derived as a basis to discriminate between the land and sea based on their spectral characteristics. Changes in waterlines over volcanic islands can provide key information to understand volcanic processes. For more info on the methodology, see Novellino et al. (2020) https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020536
-
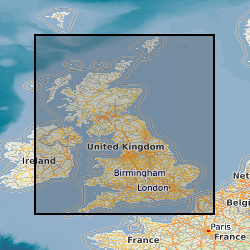
This dataset is a characterisation of discontinuity types found within rocks and soils in Great Britain. Discontinuities are breaks, fractures or planes of weakness in the rock mass. The dataset includes type, frequency and orientation of discontinuities within rock and soil materials at formation (local to regional) scale. The discontinuities are classified in 3 categories: stratification (bedding planes), foliation (mineral banding) and rock mass description. The dataset aims to facilitate the preliminary research for planning and design of buildings, infrastructure and resource extraction. It forms part of the DiGMap Plus dataset series of GIS layers which describes the engineering properties of materials from the base of pedological soil down to c. 3m depth (ie the uppermost c.2m of geology). These deposits display a variable degree of weathering, but still exhibit core engineering characteristics relating to their lithologies.
-
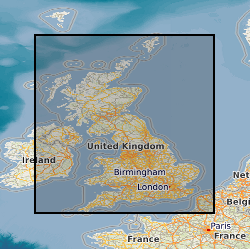
This dataset is a characterisation of the soil and rocks and the potential bulking factor (likely excavated volume increases) at Formation (local to regional) level for Great Britain. The data is categorised into Class, characteristics of similar soils and rocks and Bulking Factor, range or ranges of % bulking. The excavation of rocks or soils is usually accompanied by a change in volume. This change in volume is referred to as ‘bulking’ and the measure of the change is the ‘bulking factor’. The bulking factor is used to estimate the likely excavated volumes that will need to be moved, stored on site, or removed from site. It is envisaged that the 'Engineering Properties: Bulking of soils and rocks' dataset will be of use to companies involved in the estimation of the volume of excavated material for civil engineering operations. These operations may include, but are not limited to, resource estimation, transportation, storage, disposal and the use of excavated materials as engineered fill. It forms part of the DiGMap Plus dataset series of GIS layers which describe the engineering properties of materials from the base of pedological soil down to c. 3m depth (ie the uppermost c.2m of geology). These deposits display a variable degree of weathering, but still exhibit core engineering characteristics relating to their lithologies.
-
This dataset provides the first map and synthesis of the temperature of Britain's coalfields. It was created to support low-temperature heat recovery, cooling and storage schemes using mine water in abandoned workings. This baseline spatial mapping and synthesis of coalfield temperatures offers significant benefit to those planning, designing and regulating heat recovery and storage in Britain's abandoned coalfields. The data has been developed jointly by the Coal Authority and the British Geological Survey. It is delivered as a hexgrid representing mine water blocks, identifying equilibrium mine temperatures at 10 depth intervals (100m > 1000m) and pumped mine temperatures at 6 depth intervals (100m > 600m).
-
Hazards data in Sichuan (Dechang, Anning River catchment), China. Data include rainfall, earthquake, river catchment, boundary, geological map, soil map, land-cover map, road-map, DEM.
 BGS Data Catalogue
BGS Data Catalogue