Tectonics
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
-
Earth is a dynamic planet, for the simple reason that it is still cooling down from the heat of accretion and subsequent decay of radioactive elements. The main mechanism by which it loses heat is plate tectonics, a theory that has been widely accepted since the 1970s. The Earth is formed of a dense metallic core surrounded by a partially molten silicate mantle which itself is capped by a buoyant crust, either continental or oceanic. We live on the continental crust which largely exists above sea level. The ocean crust forms the floors of oceans and is only rarely exposed. The ocean crust forms by mantle melting at mid ocean ridges, such as the mid Atlantic ridge upon which sits the volcanic island of Iceland. New crust is constantly formed, forcing the older crust to spread outwards and oceans to grow larger. As the ocean crust spreads away from the ridge, it cools and becomes denser. Eventually it interacts with a continent, made of less dense material. The ocean crust is driven beneath the continent back into the mantle, a process known as subduction. Volcanoes form along the continental margin above the subduction zone and at least some of this activity results in addition of new continental crust. This may have been the main process responsible for initial formation and subsequent evolution of our continents. It can be observed now around the margin of the Pacific Ocean, where widespread volcanism is known as the "Ring of Fire". However, not all oceans can continue to grow! The Atlantic Ocean has stopped getting bigger as a response to the continued growth of the Pacific. Eventually, an ocean will close completely and the surrounding continents will collide, resulting in a linear mountain chain. A good example is the Himalaya, where India has collided with Asia. This whole process known as plate tectonics has a profound affect on our planet, providing us with land on which to live, seas in which to fish, freshwater to drink and our complex weather patterns. It is also a regulator of our climate since weathering of continental rocks results in drawdown of CO2 to the deep sea where it is stored. Understanding plate tectonics is central to Earth and Environmental Scientists. There are still important details that we know little about, such as how and when it began. This proposal seeks to investigate this by a novel study of critical rocks that characterise plate tectonics, in particular those that result from subduction. When ocean crust is subducted, increasing pressure and temperature change it into denser rock. As the Earth has evolved, the exact pressure and temperature conditions of this "metamorphism" have also changed. We propose to study this by using minerals that form within ocean crust during subduction. The rocks themselves are often destroyed by erosion, but tiny crystals of a robust mineral called rutile (titanium dioxide) can survive to be found in sediments derived from them. By dating these and using their chemical composition as a fingerprint, we can work out the pressure and temperature within the eroded subduction zone. Similarly, the volcanic rocks that form during subduction have changed through time. These are also often destroyed by erosion so that the exposed record may not be representative. Another robust mineral known as zircon (zirconium silicate) often survives the weathering and ends up alongside rutile in the younger sediments. Using similar methods with zircon we can also investigate changing styles of magmatism throughout Earth's history. . Currently the magmatic record implies that modern subduction began around 2500 million years ago, yet the metamorphic record implies a later start of around 700 million years ago. Our novel approach will test this. We will be able to say whether the younger date is correct and the older marks a different kind of plate tectonics, or whether the older date does indeed represent the onset of modern plate tectonics, and the exposed rock record is biased.
-
Locations of samples collected to constrain the recent activity on normal faults across Nevada. The geological samples will be used to measure the amount of exhumation that different normal faults of the Basin and Range experienced over the last 5 million years. The samples have been collected from granitic rocks that are expected to yield apatite crystals. (Uranium-Thorium)/Helium thermochronometry will be conducted on these samples to determine the cooling history of rocks from temperatures of approximately 70 degrees celsius. The samples are collected across Nevada at locations close to the fault to determine the most recent stages of exhumation. The ranges sampled are the Wassuk Range, White Range, Toiyabe Range, South Egan Range, Schell Range, Wheeler Range, House Range, Wasatch, Deep Greek, Ruby Range, Cortez Range, Humbolt Range, Dixie Valley, and Carson Range. Samples weigh approximately 2kg each. This sample coverage will constrain extension rates across the Basin and Range which is of interest to geologists, geodynamicists, and researchers interested in fault hazard.
-
Initiation files for 2D numerical models for Fluidity code. The models simulate subduction of an oceanic plate under various conditions described in Suchoy et al., 2020. The models use temperature, pressure and strain-rate dependent composite rheology, which generates different regions without prescribing material fields. The models are similar in nature to other geodynamic models (e.g. Billen and Arredondo, 2018) and can be used for further investigation of subduction dynamics, and to reproduce the results presented in Suchoy et al., 2020. For further enquiries regarding these models please contact Lior Suchoy (Imperial College London), Saskia Goes (Imperial College London) or Rhodri Davies (Australia National University).
-
A seismic dataset of 70 temporary and 3 permanent seismic stations deployed from 05/2012 to 10/2013 in northern Turkey. Three-component seismic data were collected at each location. Stations were deployed across the North Anatolian Fracture Zone (NAFZ) in the region of the 1999 Izmit and Duzce earthquakes. The network covered a footprint of ~35 by 70 km with a nominal station spacing of 7 km. Continuous seismic data were collected to study the crustal structure of the NAFZ to better understand the structure and dynamics of the NAFZ and it seismic hazard for the region. Funding for the project was provided through NERC Standard grant NE/I028017/1 and 63 stations were provided by the GEF. Additional stations were provided by the Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute. Seismic stations were a mixture of Guralp CMG-6TD and CMG-3T. Further information can be found in GEF report for loan 947 - http://gef.nerc.ac.uk/documents/report/947. Link to data: http://ds.iris.edu/gmap/YH?timewindow=2012/5/01-2013/10/01
-
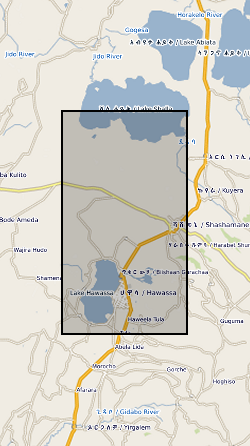
This dataset contains the locations and other pertinent information for 122 well-constrained seismic events that occurred on or near Corbetti between February 2016 and September 2017. These locations were derived from data collected on 37 broadband seismometers deployed as part of the RiftVolc project. The data were originally published in Lavayssière, A., et al. "Local seismicity near the actively deforming Corbetti volcano in the Main Ethiopian Rift." Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2019.06.008
-
The data was generated from a range of laboratory experiments where a range of silicate rocks (granite, basalt, peridotite) were crushed in oxygen-free conditions, deoxygenated water added, and the generation of hydrogen gas and hydrogen peroxide followed over a week. Results were compared to rock-free controls. The data was collected to provide insight into the production of oxidants (such as hydrogen peroxide) along tectonically active regions of the subsurface, and how the oxidants might influence subsurface microbiology.
-
In this urgency proposal we will deploy seismometers for 1 year to record aftershocks from sequence of 4 major earthquakes with magnitudes between 7.1-7.6. These recordings and other recordings of earthquakes from around the globe will allow us to delineate with high accuracy the plate interfaces of the new and old subducting slabs and image the slab structures at depth. The structure of the old and new subduction zones will illuminate the processes occurring at depth which are shifting the force balance in the region to reverse the sense of subduction. The proposed experiment will be enhanced by concurrent studies scheduled to be deployed in Fall of 2014, which includes a multimillion pound ocean bottom seismic deployment by colleagues in Japan. The combined array will allow us to image the Pacific plate which is stalling the subduction, allowing us to investigate what conditions are necessary for a plate to halt the descent of the slab into the mantle. Thus we will be able to understand how subduction stops and starts. Data available online at the Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS) Data Management Centre (DMC).
-

Data from the IODP Expedition will be archived by the International Ocean Discovery Program, including all data generated during the shipboard palaeomagnetic and magnetic anisotropy analyses and all of the logging data (FMS tool, GBM data), plus associated explanatory notes. Shore based palaeomagnetic and magnetic anisotropy data, FMS---based reorientation parameters, and downhole magnetizations inferred from modelling of the GBM borehole magnetometer data will be made available to the international community via appropriate IODP Data Reports (in addition to primary journal articles). Data Includes: Shipboard cryogenic magnetometer data Shipboard and shore based discrete sample remanence data Shipboard and shore based magnetic anisotropy data FMS---based reorientation parameters Magnetic parameters modelled using borehole magnetometer data
 BGS Data Catalogue
BGS Data Catalogue