txt
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
-
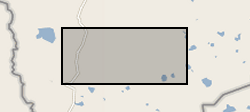
Microgravity data collected at Uturuncu Volcano between March 2010 and November 2018 The file contains microgravity data collected between March 2010 and November 2018 in the Altiplano-Puna Volcanic complex.
-
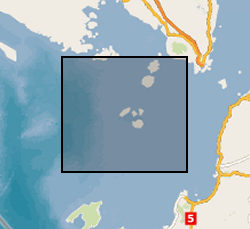
The data set comprises single channel seismic from the Sunda Strait, Indonesia. The data were acquired in 2019 to research the 1883, Krakatau volcanic eruption.
-
This dataset contains results from nanoindentation testing of five shale samples from the Horn River Basin (core from wells A100B/94 and D94A/94). The samples are from the following formations: A3 Fort Simpson, A6 Fort Simpson, D1 Muskwa, A16 Otter Park, and A20 Evie. The data is in two sets. Set 1 includes nanoindentation data from all samples, with grids conducted both parallel and perpendicular to the bedding plane. In Set 2, additional chemical analysis of select grids (on samples A3, A6 and A20) was undertaken using SEM/EDS. Both sets include the following tab-separated .txt files: grid_para.txt [Load-displacement-time data for each indent (parallel indentation)]; grid_para_summary.txt [Reduced elastic modulus, hardness and creep modulus for each indent (parallel indentation)]; grid_perp.txt [Load-displacement-time data for each indent (perpendicular indentation)]; grid_perp_summary.txt [Reduced elastic modulus, hardness and creep modulus data for each indent (parallel indentation)]. Set 2 also includes .tif files containing SEM images and EDS chemical analysis of the grids. The data has been filtered to remove indents which show 'pop-in' behaviour or time-displacement curves that do not conform to a logarithmic fit. ACKNOWLEDGMENT - The authors wish to thank the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) for funding this research through the SHAPE-UK project (grant numbers NE/R018057/1, NE/R017840/1, and NE/R017565/1), which forms Challenge 3 of the UKUH (Unconventional Hydrocarbons in the UK Energy System) programme.
-
We examine the role of cement on compaction band formation by performing triaxial tests on three sandstones, Bentheim, Castlegate and a synthetic sandstone which possess very similar porosities (~26-29%) and grain sizes (~230-300 µm), but which are cemented differently, with syntaxial quartz overgrowths, clay, and amorphous quartz cement respectively. Each sample was taken to 5% axial strain at a starting effective stress equivalent to 85% of its hydrostatic yield (P*) value, which were identified from yield under hydrostatic loading. These data for the 3 samples are presented as matlab data files. Post-deformation, each of the 3 cores underwent backscatter SEM and subsequent image analysis to examine any localised variations in porosity and grain size. These data are presented as csv files. Discrete bands form in each of the 3 sandstones but are distributed differently across each sample. Our results suggest that cement type plays a significant role in the micromechanics of deformation within each of the sandstones, which in turn, determines where the compaction bands nucleate and develop. These results may provide a starting point to investigate the role of cement on compaction localisation further.
-
This dataset includes raw point cloud data from repeat terrestrial laser scans (TLS) for a field of protodunes that developed on Brancaster Beach over a three hour period. As well as the TLS data, additional measurements of the wind speed through a 2D sonic and sediment transport on the beach and over a study protodune were collected using Wenglor fork sensors. Details on some of the methods can be found in Baddock et al. (2017; DOI: 10.1002/esp.4242). Grain size of sand on the protodune in 2016 is also included along with grain size data of saltating grains at the same site in 2019 collected using Bagnold traps.
-
This dataset includes raw point cloud data from repeat terrestrial laser scans (TLS) for dry rippled and moist sandy surfaces in the Medano Creek area at Great Sand Dunes National Park, Colorado, USA. As well as the TLS data, additional measurements of the wind speed through a CSAT 3D sonic anemometer and sediment transport using a Sensit and Wenglor fork sensors.
-

Three borehole logs are presented that describe the material excavated from a slag deposit in Consett Co. Durham (ad pdf files). The boreholes were created by GeoSonic Ltd commissioned by Cardiff University in September 2017 as part of a UKRI funded project that explores CO2 uptake in slag. The drilling penetrated through 20 and 25m of material representing the extent of the heap to underlying natural ground. The methods used and samples recovered are described in Pullin et al., 2019 Environmental Science and Technology. 53 (16) 9502-9511. DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b01265. The deposited data include photographs of recovered material from one of the boreholes.
-
Scanned and annotated thin sections, in plane-polarised and cross-polarised light. Derivative statistical data for mineral grainsize and spatial distribution. Younger Giant Dyke, Tugtutoq, South Greenland.
-
Scanned and annotated thin sections, in plane-polarised and cross-polarised light. Derivative statistical data for mineral grainsize and spatial distribution.
-

This data pack contains information from geotechnical and contaminated land investigations carried out at potential sites for the development of the UK Geoenergy Observatory in Cheshire. Following these investigations, a decision was made to move the proposed observatory to Thornton Science Park. None of the sites discussed in this data pack are in scope for development as part of the Cheshire Observatory. In total 16 holes were drilled using a variety of techniques. The only hole to be drilled using rotary coring was BHA-101. This borehole was cored extensively and logged with wireline geophysical tools. As such this is the main focus of the data pack. BHA-101 was drilled to TD of 121.2 m between 19-Nov-2020 and 09-Dec-2020. Drill core was collected from 51 m – 121 mm with 100 mm diameter. This initial data release pack from BGS contains composite and digital wireline logs alongside daily driller's borehole records.
 BGS Data Catalogue
BGS Data Catalogue