2021
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Service types
-
The BGS Permeability Index dataset shows estimated rates of water movement from the ground surface to the water table. The v8 dataset incorporates the latest geology mapping (BGS Geology 50k). This includes updates to the lithology-coding schema, the LEX_RCS. A 2-part code used to identify the named rock unit from the BGS lexicon of named rock units (LEX) followed by a Rock Classification Scheme (RCS) code which describes the rocks lithological characteristics e.g. texture and composition. Updates to these codes and latest dissolution hazard data sourced from BGS GeoSure: Soluble Rocks have been reviewed and classified as part of the version 8 release. The dataset covers Great Britain and is presented at a scale of 1:50 000, based on the geological data at the same scale. However, in areas where the geology is not mapped to this scale, the next best available scale is used. The BGS Permeability Index can be used to compare the relative permeability of deposits at the regional scale, indicating where highly permeable rocks could allow rapid infiltration to occur, or where less permeable rocks are present and water could pond on the ground surface. The dataset can be used as a component in a wide range of geo-environmental assessments such as natural flood management, Sustainable Drainage Systems, engineering desk studies, slope stability, and aquifer vulnerability. It is for use at the regional scale and is not recommended for use at the site-specific scale.
-
The property subsidence assessment dataset provides an understanding of the shrink-swell hazard at both the individual property and/or postcode level for England and Wales. It builds upon the BGS GeoSure shrink-swell data by mapping the hazard to the individual building polygon and considering the other susceptibility factors of building type, foundation depth, and drainage and tree proximity. The data consist of GIS building polygons with an overall susceptibility to subsidence score between 1-100. Scores are also classified from non-plastic to very high. Each building polygon is also scored from 1-10 for each subsidence factor (geology, foundation, drainage, building type, building storey and tree proximity). Postcode data is also available as a table showing the ‘average’ PSA score for all buildings within the postcode. The identification of shrink-swell related subsidence prone areas, alongside the inclusion of potential sources to exacerbate these phenomena, can better inform insurers and homeowners and form the basis to make decisions concerning prevention and remediation. The product enhances geological information obtained from GIP (BGS GeoSure Insurance Product) and GeoSure via the inclusion of the crucial shrink-swell susceptibility factors (proximity to trees and foundation depth). This therefore allows the derivation of a risk element for the housing stock at Building level, which is then generalised to Postcode level. BGS GeoSure - a series of GIS digital maps identifying areas of potential natural ground movement hazard in Great Britain
-

These images were acquired using micro computed tomographic imaging of 7 sandstone plugs taken at various depths in the Sellafield borehole 13B. SF696 (63.8 m), SF697 (76.1 m), SF698 (96.98 m), SF699 (126.27 m), SF700 (144.03 m), SF701 (172.16 m) and SF702 (181.39 m). These samples are further detailed and analysed in the following article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1144/petgeo2020-092
-
The dataset consists of data for the UK for the Sustainable Development Goal 6.6.1: groundwater sub-indicator for the period 1990 to 2019. The dataset reports for the UK against Sub-Indicator 5 of Goal 6.6.1, following the recommended procedures in the UNEP report on monitoring methodologies for that sub-indicator. The sub-indicator is defined as the change in mean groundwater levels, averaged over a five-year period, from a mean in levels over a previous five-year reference period. Groundwater level data was obtained from BGS’ WellMaster database. 192 groundwater level monitoring stations were processed and, following quality control, 154 were used to provide estimates of regional variation in groundwater levels for 19 of the 34 HydroBASINS at Level 6 in Great Britain and Northern Ireland. As required by the guidance in the monitoring methodology, the sites chosen are representative of local and regional groundwater systems and are observation and monitoring boreholes where groundwater levels are not systematically affected by abstraction. All sites chosen have average monitoring frequencies of greater than one observation a month. The dataset is provided as a .csv file with the following headers: Column A: HYBAS_ID, HydroBASIN unique identification number. Column B: reference period (1990 to 1994). Columns C to AA: reporting periods (five-year periods starting in 1991) with data reported as percentage change (relative to reference period) in running mean five-year groundwater level by HydroBasin.
-
Soil prediction maps for 56 chemical elements, pH and organic matter content have been produced using machine learning analysis in western Kenya. The predictive maps were based on 452 soil samples collected across western Kenya during field surveys carried out between 2015 and 2020. Samples were analysed by the inorganic chemistry laboratories at the British Geological Survey. The maps, created using random forest machine learning algorithms, are displayed as raster files with a spatial resolution of 500m. The samples were collected as part of a geochemistry and health project to investigate the spatial incidences of diseases in the Rift Valley (e.g. oesophageal cancer, iodine/zinc deficiency), which included a range of data and sample collections to inform sources of micronutrients or exposure to potentially harmful elements, with outputs to inform agriculture and public health practitioners. These predictive maps provide a baseline geochemistry survey for the agri-community, academics and public health officials.
-
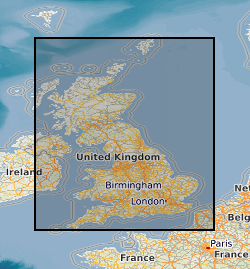
Radon is a natural radioactive gas, which enters buildings from the ground. The joint UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) (formerly Public Health England (PHE)) - British Geological Survey (BGS) digital dataset Radon Potential for Great Britain provides the current definitive map of radon Affected Areas in Great Britain. Exposure to high concentrations increases the risk of lung cancer. UK Health Security Agency (formerly PHE) recommends that radon levels should be reduced in homes where the annual average is at or above 200 becquerels per cubic metre (200 Bq m-3). This is termed the Action Level. The UKHSA defines radon Affected Areas as those with 1% chance or more of a house having a radon concentration at or above the Action Level of 200 Bq m-3. The dataset allows an estimate to be made of the probability that an individual property is at or above the Action Level for radon. This information provides an answer to one of the standard legal enquiries on house purchase in England and Wales, known as CON29 standard Enquiry of Local Authority; 3.13 Radon Gas: Location of the Property in a Radon Affected Area. Radon Potential for Great Britain also provides information on the level of protection required for new buildings as described in the latest Building Research Establishment guidance on radon protective measures for new buildings (Radon: guidance on protective measures for new dwellings; BR 211, 2015 in Scotland, England, Wales and Northern Ireland). This radon potential hazard information for Great Britain is based on UKHSA indoor radon measurements and BGS digital geology information. This product was derived from BGS Geology 50k (formerly known as DigMap50k) version 8 and UKHSA in-house radon measurement data. The indoor radon data is used with the agreement of the UKHSA. Confidentiality of measurement locations is maintained through data management practices. Access to the data is under licence.
-
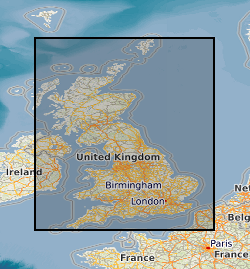
Radon is a natural radioactive gas, which enters buildings from the ground. The joint UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) (formerly Public Health England (PHE) ) - British Geological Survey (BGS) digital Indicative Atlas of radon in Great Britain presents an overview of the results of detailed mapping of radon potential, defined as the estimated percentage of homes in an area above the radon Action Level. Exposure to high concentrations increases the risk of lung cancer. UKHSA (formerly PHE) recommends that radon levels should be reduced in homes where the annual average is at or above 200 becquerels per cubic metre (200 Bq m-3). This is termed the Action Level. UK Health Security Agency defines radon Affected Areas as those with 1% chance or more of a house having a radon concentration at or above the Action Level of 200 Bq m-3. The Indicative Atlas of radon in Great Britain presents a simplified version of the radon potential for Great Britain with each 1-km grid square being classed according to the highest radon potential found within it, so is indicative rather than definitive. The joint UKHSA-BGS digital radon potential for Great Britain provides the current definitive map of radon Affected Areas in Great Britain.
-
This web service shows the centroids for countries for which there are minerals statistics data (Imports, Exports, Production) in the World Mineral Statistics database. A GetFeatureInfo request can retrieve some of the data for the country queried, but to get all data you should used the associate WFS.
-
This service provides access to the World Mineral Statistics database data.
-

The data set presents major and trace element geochemical data obtained from ICP-MS measurements on micro-drilled subsamples of ferromanganese (Fe-Mn) crusts from Tropic Seamount, north-east Atlantic Ocean. The data represent detailed stratigraphic analysis of Fe-Mn crust samples 078_019 and 085_004. These samples were collected at 3100 and 1100 meters beneath sea level, respectively, during the JC142 expedition of the RRS James Cook for the MarineE-Tech project in 2016.
 BGS Data Catalogue
BGS Data Catalogue